HowTo Configure Linux LVM with Multipath Enabled
In this article, your going to learn HowTo Configure Linux LVM Multipath Enabled. Before We published about What is LVM (Logical Volume Manager). Creating LVM itself you have the flexibility to increase/decrease disk space as per the requirement, but why we have to create Multipath for SAN Disks.?
Actually, DM Multipath is used to fail over when one path is failed, it will use another path to send application I/O through multipath (Active/Passive). Another way of using is load sharing when one path is full with I/O it redirect the traffic with another path (Active/Active)
What is Multipath and How it will be useful
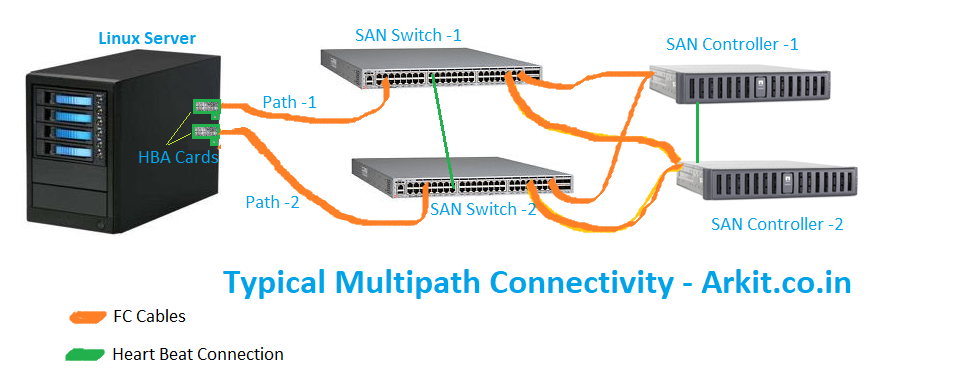
As shown in above diagram, Linux server is connected to SAN Storage with dual paths (path-1 and path-2). If you map an LUN from SAN Device it will show in Linux server as two disks because it is coming from two HBA cards (typically two paths). Here our goal is to combine both the paths and use them as single path (redundancy).
Always do not trust (dependent) single cable connectivity because
- If FC Cable Fails.?
- HBA Card Failure.?
- SAN Switch Failed.?
If any one the component fails, you loose Disk from your Linux Server as a result hosted application will go down. Now do you understand how CRITICAL is SAN Disk.
Above is the diagram which shows Data flow from Applications to LUN/SAN Storage after multipath configuration
HowTo Install and configure Multipath RHEL 7
To configure multipath in Linux few packages you have to install
# yum install -y device-mapper*
Verify installed packages using rpm command
# rpm -qa |grep device-mapper device-mapper-persistent-data-0.6.3-1.el7.x86_64 device-mapper-multipath-0.4.9-99.el7.x86_64 device-mapper-libs-1.02.135-1.el7.x86_64 device-mapper-event-1.02.135-1.el7.x86_64 device-mapper-1.02.135-1.el7.x86_64 device-mapper-event-libs-1.02.135-1.el7.x86_64 device-mapper-multipath-libs-0.4.9-99.el7.x86_64
Now do not start multipathd service, we have to copy the multipath config file from /usr/share/doc/device-mapper-multipath-0.4.9/multipath.conf location to /etc/multipath.conf Or you can also generate using simple multipath command
[root@ArkItServ yum.repos.d]# systemctl start multipathd [root@ArkItServ yum.repos.d]# systemctl status multipathd.service ● multipathd.service - Device-Mapper Multipath Device Controller Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/multipathd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) Condition: start condition failed at Thu 2017-08-17 19:04:38 IST; 7s ago ConditionPathExists=/etc/multipath.conf was not met
Generate Multipath Configuration file using below command and start multipathd service
# mpathconf --enable --user_friendly_names y
[root@ArkItServ ~]# modprobe dm_multipath [root@ArkItServ ~]# lsmod |grep dm_multipath dm_multipath 23065 0 dm_mod 114430 23 dm_multipath,dm_log,dm_persistent_data,dm_mirror,dm_bufio,dm_thin_pool
HowTo Configure Linux LVM Multipath
Map the LUN from SAN Storage to Linux Server using FCP protocol
Scan for New devices using below command
ls /sys/class/scsi_host/ | while read host ; do echo "- - -" > /sys/class/scsi_host/$host/scan ; done
Now verify multipath disks automatically get friendly name you already enabled in multipath configuration
If you exclude few devices list by specifying block list they will not show in multipath command list
Use multipath alias section to specify alternative name to override friendly name. Below is the actual /etc/multupath.conf file
### Default Multipath configuration RHEL 7 ###
defaults {
udev_dir /dev
polling_interval 10
selector "round-robin 0"
path_grouping_policy failover
getuid_callout "/sbin/scsi_id -g -u -s /block/%n"
# prio_callout "/sbin/mpath_prio_ontap /dev/%n"
prio_callout /bin/true
path_checker readsector0
rr_min_io 100
max_fds 8192
rr_weight priorities
failback immediate
# no_path_retry fail
user_friendly_names yes
}
## Device Blacklist Rule ##
blacklist {
devnode "sd[a]$"
devnode "^(ram|raw|loop|fd|md|dm-|sr|scd|st)[0-9]*"
devnode "^hd[a-z]"
devnode "^cciss!c[0-9]d[0-9]*[p[0-9]*]"
}
## Multipath Aliases ###
multipaths {
multipath {
wwid 4500a098038303635685d472f492d6b5q
alias DATA-DISK
path_grouping_policy failover
# ONTAP Path: ark-netapp-03:/vol/prod_ora_disk1/prod_disk1
# LUN: 1
# LUN Size: 500g
# Host Device: mpath1(4500a098038303635685d472f492d6b5q)
# 5:0:0:5 sdp
# 6:0:0:5 sdq
# 6:0:1:5 sdaa
# 5:0:1:5 sdr
}
}
Now check new changes using multipath -v2 command
- -v level
- verbosity, print all paths and multipaths
- 0 no output
- 1 print the created or updated multipath names only, for use to feed other tools like kpartx
- 2 + print all info : detected paths, coalesced paths (ie multipaths) and device maps
Add Partition Mappings using kpartx command
# kpartx -a /dev/mapper/DATA-DISK
Verify the device mapper
# ls -al /dev/mapper/
Create Linux LVM partition using fdisk utility
# fdisk /dev/mapper/DATA-DISK :n :p Enter Enter t 8e :wq
Start Creating Linux LVM using multipath disk
# pvcreate /dev/mapper/DATA-DISKp1 Writing physical volume data to disk "/dev/mapper/DATA-DISKp1" Physical volume "/dev/mapper/DATA-DISKp1" successfully created
Physical volume is created successfully, using multipath Linux LVM
# vgcreate DATAVG /dev/mapper/DATA-DISKp1 Volume group "DATAVG" successfully created
Volume Group has created using Multipath PV
# lvcreate -n LV03 -l 100%FREE DATAVG Logical volume "LV03" created
Logical Volume with 100% free space now in place.
Format Newly created Logical Volume using below command
# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/DATAVG/LV03
You have successfully configure Linux LVM Multipath
Mount formatted partition and use it
# mount /dev/DATAVG/LV03 /mountpoint
Permanent mount add entry in fstab file
/dev/DATAVG/LV03 /mountpoint ext4 defaults 1 2
That’s All we achieved is redundant disk path in case of one path failure.
Related Articles
shell scripting very basics to learn
RHCSA Certifiation Guide Written by Ravi Kumar
Thanks for your wonderful Support and Encouragement
- Get Email | Download E-Books
- Facebook Page
- Youtube Channel
- Exclusive Telegram Group
- Discuss On WhatsApp Group










Nice techie information Ravi.. Thank you for sharing
Very useful content ARK..
Thanks for sharing.. well explained..
Thank you. DurgaPrasad
Nice 🙂