ss utility to investigate sockets RHEL 7/Centos 7/Fedora 24
ss utility to investigate sockets statistics in RHEL 7 / Centos 7 / Fedora 24 Operating systems. ss utility / command is similar to netstat command. ss can display more TCP and state information than other tools. Let’s see how we can utilise this ss utility.
ss utility to see all TCP connections
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -at State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 50 *:mysql *:* LISTEN 0 50 *:netbios-ssn *:*
State
- LISTEN – Socket is in listening state
- UNCONN – Connection not established
- ESTAB – Connection established
Recv-Q – Received
Send-Q – Sent
Local Address:port – Local machine address and port number
Peer Address:port – Destination Address and Port number
Local Address:port → Peer Address:port
Do not resolve service names
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -n
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -au
above command will list all UDP connections
List all listing processes
Show process using socket
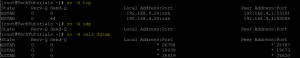
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -p
Print summary statistics
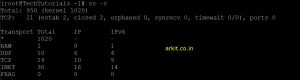
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -s Total: 950 (kernel 1020) TCP: 21 (estab 2, closed 2, orphaned 0, synrecv 0, timewait 0/0), ports 0 Transport Total IP IPv6 * 1020 - - RAW 1 0 1 UDP 10 6 4 TCP 19 10 9 INET 30 16 14 FRAG 0 0 0
in this we can see how many TCP connection, INET connections and RAW all the details we can get as a summary using above command
Query Socket
List of socket tables to dump, separated by commas. The following identifiers are understood: all, inet, tcp, udp, raw, unix, packet, netlink, unix_dgram, unix_stream, packet_raw, packet_dgram.
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -A tcp [root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -A udp [root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -A unix_dgram
Dump raw information to file
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss --diag=test1
Above command will not display anything on stdout / output which just dump the information to specified file
Apply filter as you required
FILTER := [ state TCP-STATE ] [ EXPRESSION ]
To display all established ssh connection statistics
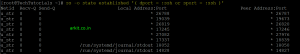
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -o state established '( dport = :ssh or sport = :ssh )'
ss -x src /tmp/.X11-unix/*
Find all local processes connected to X server.
ss -o state fin-wait-1 '( sport = :http or sport = :https )' dst 193.233.7/24
List all the tcp sockets in state FIN-WAIT-1 for our apache to network 193.233.7/24 and look at their timers.
Socket extended details
[root@TechTutorials ~]# ss -e Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port u_str ESTAB 0 0 * 26788 * 26787 <-> u_str ESTAB 0 0 * 19039 * 19673 <->
Conclusion
ss (socket statistics) utility to investigate sockets. More extended details which not cover in netstat command
That’s it about ss utility / command
Related Articles
ls command with 25 practical examples
Thanks for your wonderful Support and Encouragement
- Get Email | Download E-Books
- Facebook Page
- Youtube Channel
- Exclusive Telegram Group
- Discuss On WhatsApp Group