cp command 15 Practical Examples Copy Files Linux
cp command is used to copy the files and directories from SOURCE to DESTINATION. You can use multiple source paths and one destination path. copy command alone can’t copy files from one source to multiple destinations, if you want to copy files from one source to multiple destination using cp command you can combine with xargs or for loop you can do it.
cp command 15 practical examples
Syntax:
cp [OPTION] SOURCE DEST
Very first example without using any options file can copy from one location to another location within same server
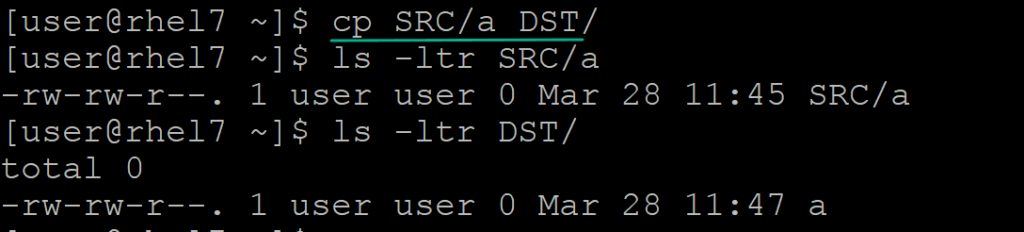
arkit$ cp SRC/a DST/
above command copied the file a but file property has changed in destination
# cp -a SRC/b DST/
Option -a means archiving content and not exactly copy
Create backup files when your copying same named files to destination. This option will not overwrite files. In destination directory backup file will be renamed or extended with (~) tild sign.
$cp --backup SRC/e DST/
Don’t Copy content Copy file Attributes
cp --attributes-only cp/test2.txt dst/
As shown above Don’t copy the file data, just the attributes.
In other way copy content of the special file don’t copy it’s properties
cp --copy-contents /etc/passwd /tmp/
Create Hard Links and Soft Links
Along with cp command using -l will create hard link and -s will create soft link
cp -l cp/test4.txt dst/
Creating hard link is keeping destination file updated with lasted data of source automatically, when you delete either of the file another file is available for you
cp -s /src/test.txt /tmp/test.txt
Preserve file properties while copying
Using –preserve=Attributes like (mode,ownership,timestamps, context,links, xattr, all)
which file property you want to preserve after copy mention and preserve it.
Copy Directories using cp command in Linux
To copy directories using cp command in Linux, add option -R or -r
[user@rhel7 ~]$ cp SRC/dir1/ DST/ cp: omitting directory ‘SRC/dir1/’ [user@rhel7 ~]$ cp -R SRC/dir1/ DST/
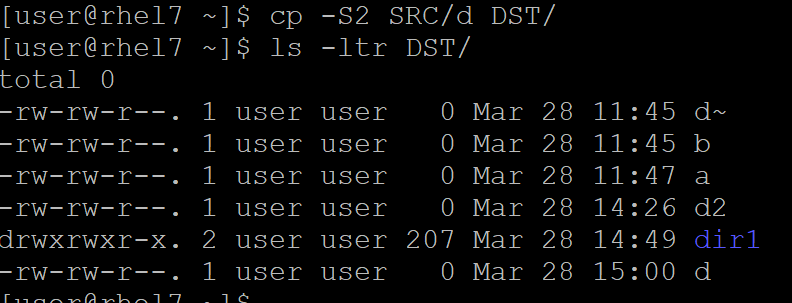
override the usual backup suffix. We already saw when using –backup it will create an files with (~) to make them as backup files. -S option give us to replace ~ with any other character or number
@rhel7 ~]$ cp -S2 SRC/d DST/
Update destination file when source file is updated, without replacing/overwriting
cp -u SRC/k DST/
Option -u = Update
Apply SELinux context to file using cp command
cp -Z /root/data* /tmp
last and final option to know cp command core utility version
cp --version
Conclusion
Copy files and directories in different way with different options, most of the cases Linux administrators use cp -R, cp -p and cp -a.
Related Articles
Everything Linux tutorial what you need for your career
chmod command to change file permissions
100 Linux commands Video tutorial
Thanks for your wonderful Support and Encouragement
- Get Email | Download E-Books
- Facebook Page
- Youtube Channel
- Exclusive Telegram Group
- Discuss On WhatsApp Group